What is Keto?
“Keto” is short for the ketogenic diet.
The keto diet was the number one health-related search term on Google’s 2018 list and came in second in 2019.
The keto diet is very different from the average American diet because it relies on fat rather than carbs as the main source of calories.
Carbs (carbohydrates) = sugar, pasta, potatoes, bread, rice
The keto diet seems to go against all diet logic because instead of cutting out fat, you eat large amounts of fat for every meal.
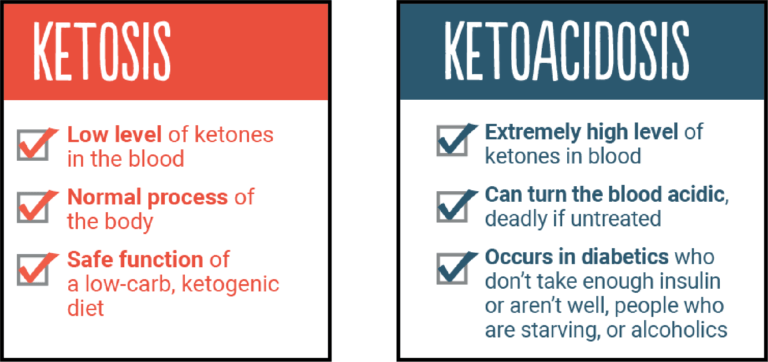
The diet is high in fats and very low in carbs which forces the body into a state known as ketosis
Ketosis causes the body to break down body fat
It typically takes 3-4 days to reach a state of ketosis
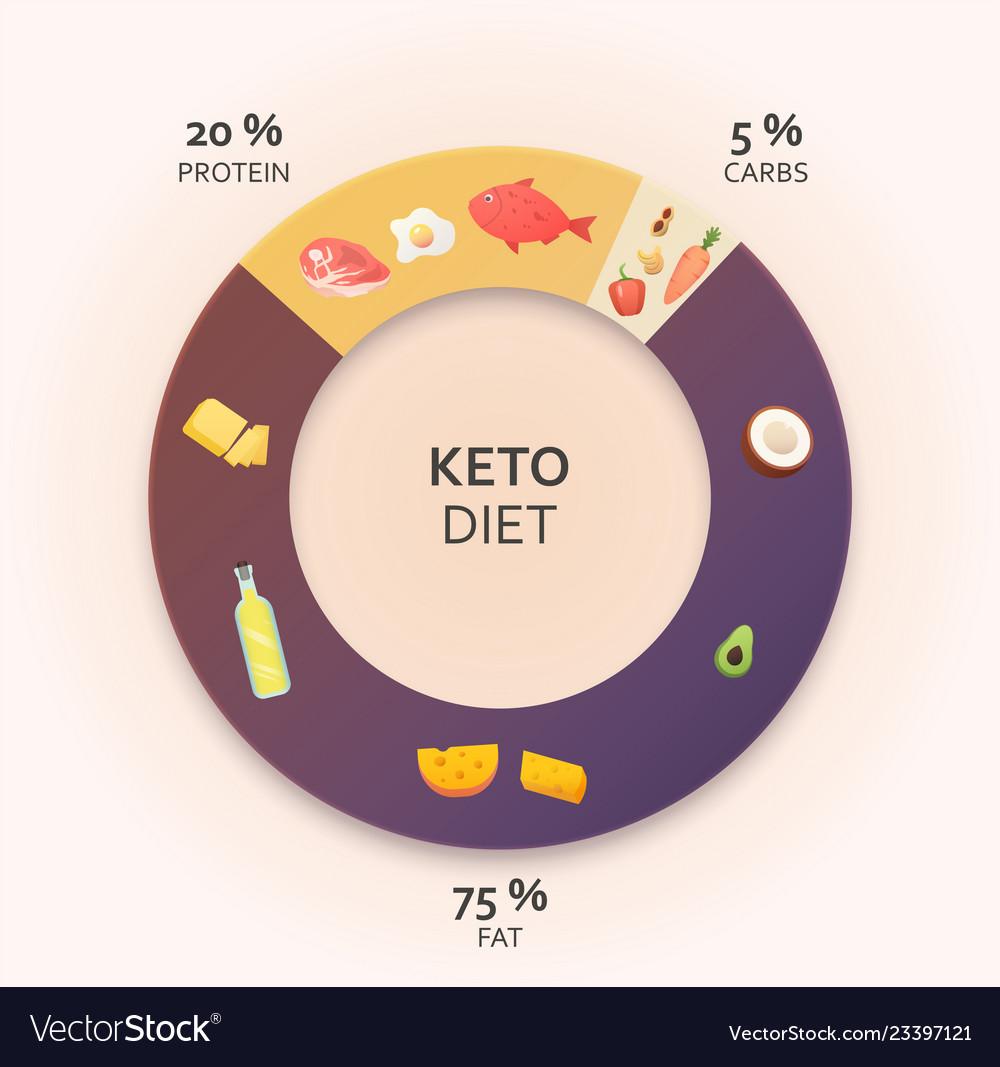
The Keto diet recommends:
Fat calories about 70% of daily caloric intake
Carbohydrate calories of 5% of daily caloric intake, around 15 to 20 net carbs a day (1 apple or 1 banana a day)
Proteins are about 20% calorie intake
The government’s 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends people receive up to 65% of daily caloric intake from carbs and less than 10% from saturated fats. (opposite of keto)

* Children, teens, and people at risk of heart rhythm problems should not try the keto diet.
How does Keto cause Weight Loss?
When you follow the keto diet, your body stops relying on carbs (sugar) as the main source of energy; Instead, it uses body fat for energy. Ketones are produced from the breakdown of the stored fat in the liver, which sends your body into ketosis. This can lead to a loss of body fat.
When you eat less than 50 grams of carbs a day, your body eventually runs out of fuel (blood sugar) it can use quickly. This typically takes 3 to 4 days. Then you’ll start to break down protein and fat for energy, which can make you lose weight.
It’s important to note that the ketogenic diet is a short term diet that’s focussed on weight loss rather than the pursuit of health benefits.
How much Weight Can I Lose on a Keto diet?
When following the keto diet, weight loss can vary from person to person. When people with excess weight begin a ketogenic diet, they typically lose about 6 to 8 pounds the first week, then about 1 to 2 pounds per week until a plateau is reached and weight loss lessens.
The initial weight loss is partly due to losing water weight.
How do you start a keto diet?
“If you are considering starting any kind of ketogenic diet, you should discuss it first with your doctor. The diet may be harmful if you have existing kidney, liver or heart disease. If you have diabetes or high blood pressure and are on medications, you should be in close contact with your physician to monitor changes and adjust medications as needed,” says Diane Vizthum, a dietitian at the Adult Epilepsy Diet Center at Johns Hopkins.
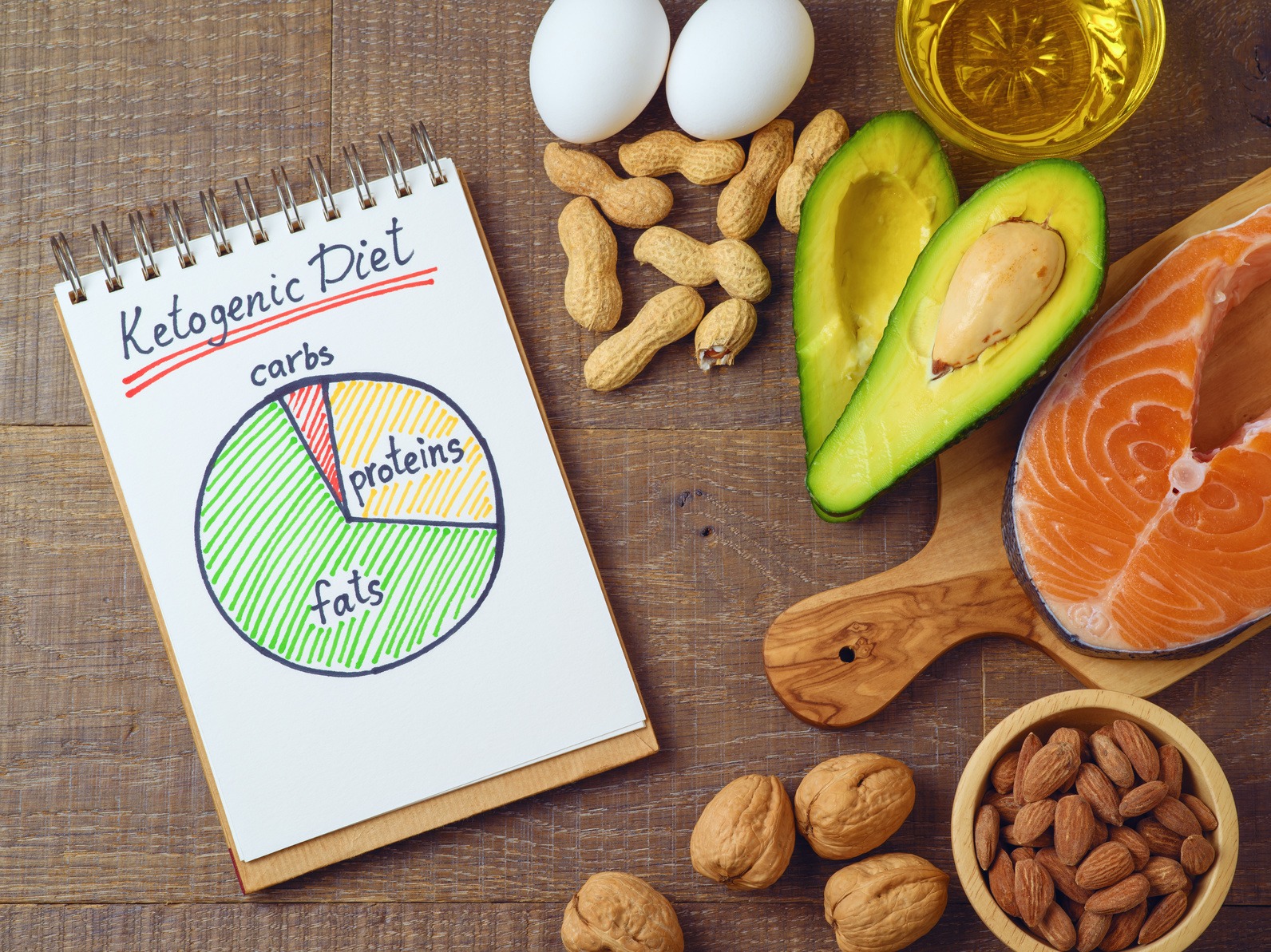
What do you eat on keto?
 from delish.com
from delish.com
In a daily 2,000-calorie diet, you would eat about 165 grams of fat, 25-40 grams of carbs, and 75 grams of protein; However, the exact ratio depends on your particular needs.
Common keto foods include:
- Meat
- Eggs
- Full-fat dairy including butter and cream
- Leafy greens and non-starchy vegetables (kale, spinach, swiss chard), broccoli, asparagus, cauliflower, brussels sprouts, onions, bell peppers, garlic, mushrooms, cucumber, celery. A cup of chopped broccoli has about six carbs. (max daily carbs are about 25-40 grams)
- Nuts (almonds and walnuts) & seeds
- Avocados
- Tofu
- Olive Oil
- Small amounts of berries
How do you know you’re in ketosis?

There are several ways to figure out if you’re in ketosis (meaning you are burning fat in your body).
The easiest way is to pay attention to symptoms, which tend to include bad breath, increased urination, and dry mouth.
If you want to get even more accurate, there are blood and urine tests for those on the keto diet. They are available at drug stores, buy a box of urine strips designed for diabetics or use a glucose or ketone meter for more accurate results. Test for ketones in your urine or blood to see if you are in ketosis.
What are the benefits of Keto?
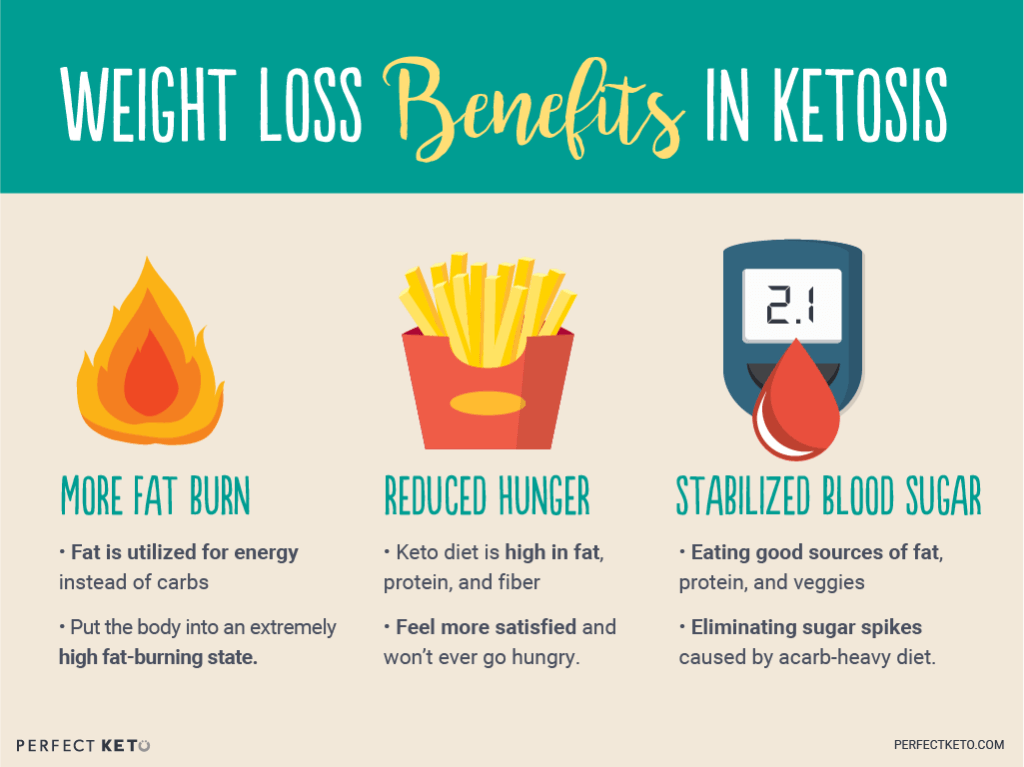
One of the main weight loss mechanisms related to the keto diet is its ability to reduce hunger. Following the ketogenic diet has been linked to decreased levels of ghrelin, one of your body’s main hunger hormones. Reducing ghrelin levels and hunger can cause you to eat fewer calories throughout the day, which may result in weight loss.
Another potential benefit of keto is weight loss through the loss of water weight that comes from the lower carb intake.
Keto and Diabetes
Keto may help improve medical conditions related to obesity like type 2 diabetes, because, on keto, your body may also become more sensitive to insulin, a hormone that helps balance your blood sugar. A 2017 review of nine studies found that people with type 2 diabetes on a low-carb diet generally could control their blood glucose levels better than diabetes patients on either a normal or high-carb diet.
Low-carb diets seem to help keep your blood sugar lower and more predictable than other diets. But when your body burns fat for energy, it makes compounds called ketones. If you have diabetes, particularly type 1, too many ketones in your blood can make you sick. So it’s very important to work with your doctor on any changes in your diet.
Is the Keto diet hard to maintain?
The keto diet can be very restrictive and may be difficult for people to stick to. The average ‘healthy’ person probably does not need to follow a keto diet but could probably benefit from reducing the intake of refined/processed carbohydrates.
What is the difference between Keto and Atkins?
Atkins and keto are both low-carb diets that may help with weight loss, diabetes management, and heart health.
Their main difference is that you gradually increase your carb intake on Atkins, while it remains very low on the keto diet, allowing your body to stay in ketosis and burn ketones for energy. (healthline.com)
Who shouldn’t try the keto diet
Keto isn’t for everyone.
Kids: Nutritionists say that putting children or teens on the keto diet — or basically any restrictive diet — can lead to nutritional deficiencies and eating disorders.
Heart Rhythm Problems: Keto isn’t great long-term if you have, or are at risk of, heart rhythm problems. A large 2019 study, published by the American College of Cardiology, that involved medical records of nearly 14,000 people reported that people who don’t consume many grains, fruits, and starchy vegetables for years at a time, are at a higher risk of developing a heart condition called AFib.
Bottom line: The keto diet is not for everyone and you should speak with a certified nutritionist or doctor before starting it, especially if you have a medical condition.
What are the risks of keto?
Increase in “bad” LDL cholesterol, which is also linked to heart disease.
Vitamin Deficiencies: Even if you’re otherwise healthy, long-term keto could lead to vitamin B and C deficiencies, since many foods rich in these vitamins — like beans, legumes, and fruit — are also high in carbs.
Liver problems. With so much fat to metabolize, the diet could make any existing liver conditions worse.
Kidney problems. The kidneys help metabolize protein and the keto diet may overload them.
Constipation. The keto diet is low in fibrous foods like grains and legumes.
Fuzzy thinking and mood swings. The brain needs sugar from healthy carbohydrates to function. Low-carb diets may cause confusion and irritability.
Make sure that you talk to a doctor and a registered dietitian before ever attempting a ketogenic diet.
What are the Side Effects of Keto?

Most common:
Constipation,
Low Blood Sugar
Indigestion
Bad breath
Less common but more serious:
Acidosis: high levels of acid in your body
Keto flu: which may include headache, weakness, and irritability
Kidney stones 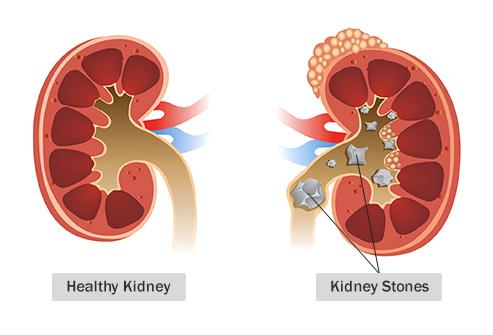
Photo credit: WebMD.com
References
https://www.insider.com/what-is-keto-diet
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/should-you-try-the-keto-diet
https://www.cnet.com/how-to/how-to-go-keto-a-beginners-guide-to-the-keto-diet/
https://www.webmd.com/diet/ss/slideshow-ketogenic-diet
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/does-keto-work#weight-loss


